For industries that use the Big-Bag system, we have machinery for loading and unloading maxi-bags. We also provide the pneumatic conveying and handling systems necessary for the insertion of its contents into the production line.
Due to their weight, it is very important to take into account all the necessary safety requirements when loading, moving and unloading these bags inside the plant. With this in mind, we produced the DBB maxi-bag unloader, specially designed to simplify unloading, and make it a simple and safe operation, thus avoiding accidents, product waste and dust suspension in the environment.


Equipment available for loading and unloading big bags:
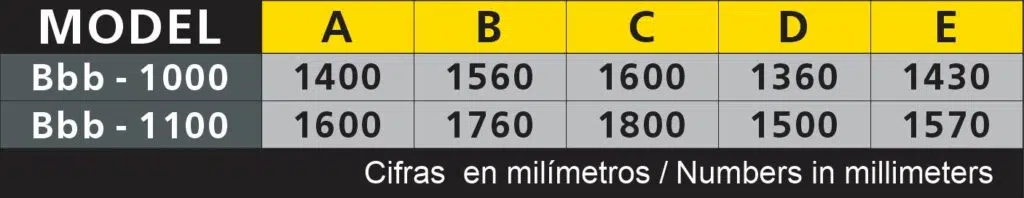
1- DBB big-bag Unloader
If you need equipment to unload big bags quickly and efficiently, we have a product to fit your needs: the DBB Unloader.
Its proven design makes the unloading of maxi bags a simple and safe operation, guaranteeing the absence of dust in the environment and avoiding the waste of raw materials.
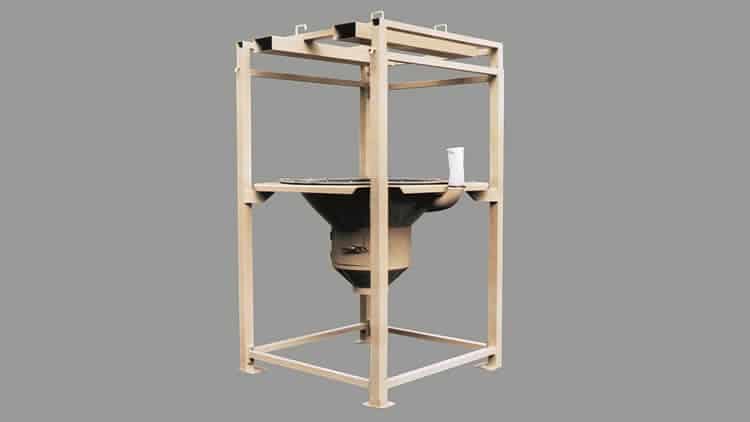

The unloading system is composed of:
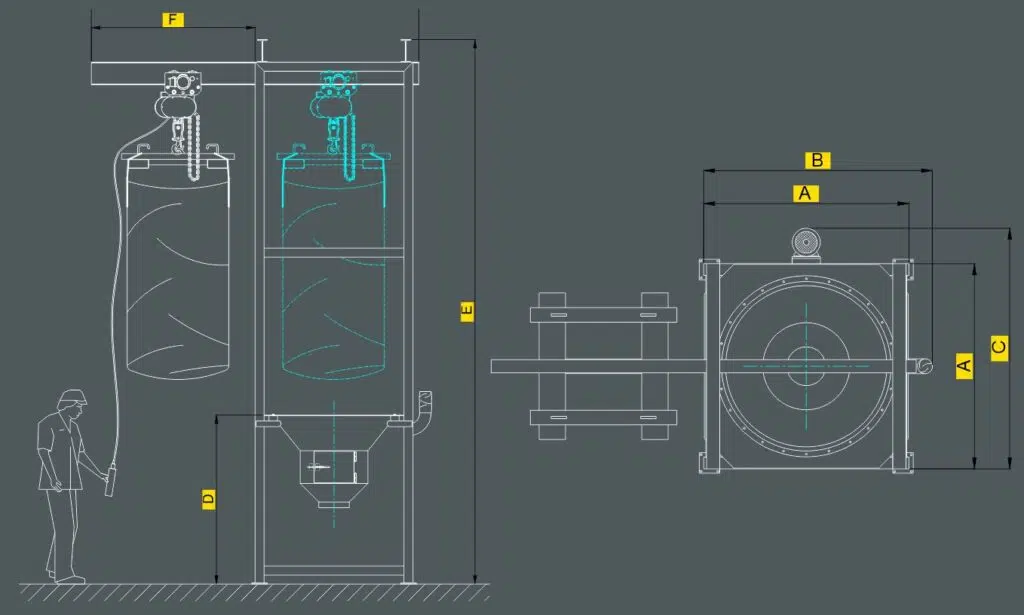
A modular structure adjustable in height; a base with a conical hopper of 1, 2 m3 capacity with optional vibration; a breathing spout with filtering sleeve and a lower door to open and unload the maxi-bags without the possibility of accidents. It can be built in different materials – such as iron or stainless steel – and with various accessories that facilitate the emptying of the big-bags.
Among the latter, we highlight the self-supporting rigging that lifts and positions the bags for unloading, the automatic cutting system and the shaking system that significantly reduces big-bag emptying times in the case of products that clump together.
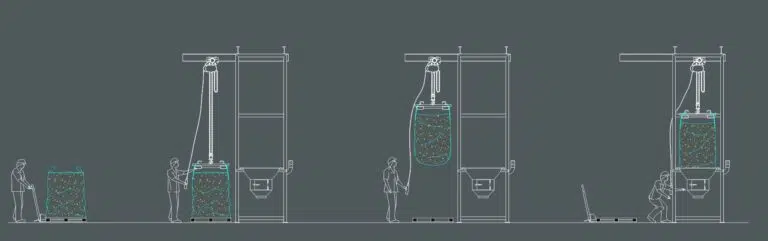
DBB Big Bag Unloader Mode of Operation
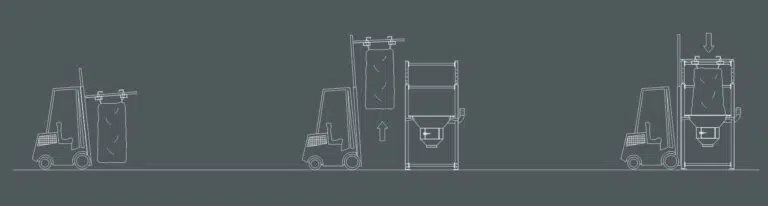
1.The operator hangs the big bag, placing his ears on the hooks of the “hanger”, which must be previously placed on the forklift’s claws. It is important to use this mode of transfer to ensure safety.
2.The forklift lifts the big bag and approaches it, entering the structure of the DBB big bag unloader.
3.The forklift gently lowers the big bag until the “hanger” rests on the height-adjustable structure and is withdrawn, leaving the hanger hanging. At that moment the big bag is ready for the operator to open it and start unloading.
4.Once the unloading is finished, the forklift picks up the hanger again and lowers it to remove the empty big bag and hang a full one.
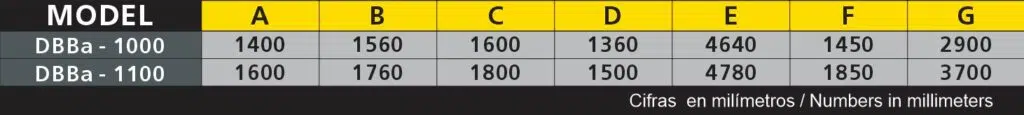
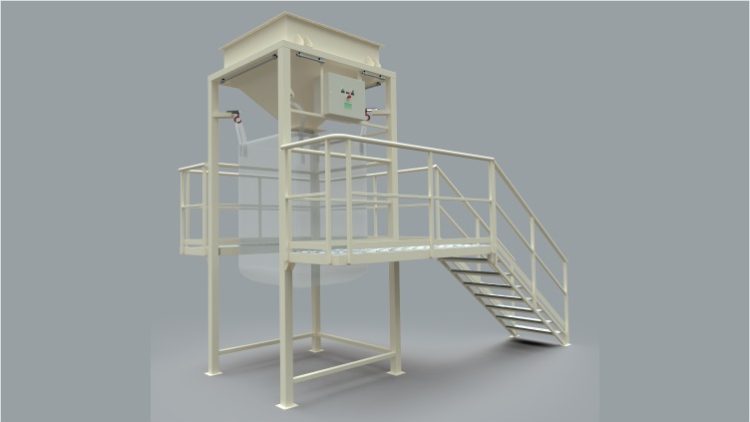
2- DBBa Big-Bag Unloader with hoist
The unloader with integrated hoist allows you to avoid the use of a forklift for the big bag unloading operation. In other details, it is a very similar machine to the DBB Big Bag unloader.
To determine the most appropriate hoist, the following should be analyzed:
- Weight of the largest Big Bag to be used.
- If you wish to have manual or electric elevation.
- If you want to have manual or electric translation.
DBBa Big Bag Unloader Operation Mode
- The operator moves the big bag with a pallet truck and leaves it in the lifting area of the hoist.
- Then place the ears on the hooks on the “perch” that must be previously hung.
- Manually or electrically, the operator places the Big bag in position for opening and unloading.
- Once unloading is complete, the rig is ready to move into position to remove the empty big bag and hang the next full one.
3- Big Bag Loader
We basically manufacture 2 types of chargers:
The big bag loader has been designed for the correct and safe filling of BIG-BAGS, avoiding accidents, product waste and dust in the environment.
– The CBBG charger is the one that fills it commanded by the scale from where the big bag hangs.
– The CBBV charger in which the filling is by volume and where the stop order is given by a level control.
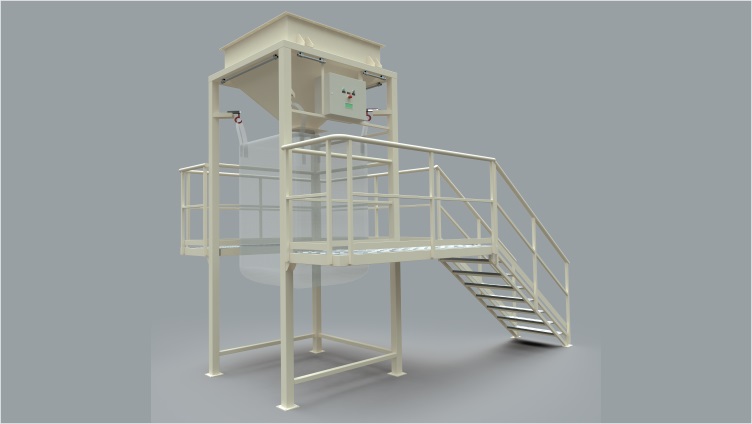

Design details and components of the big bag or maxi-sack filler loader
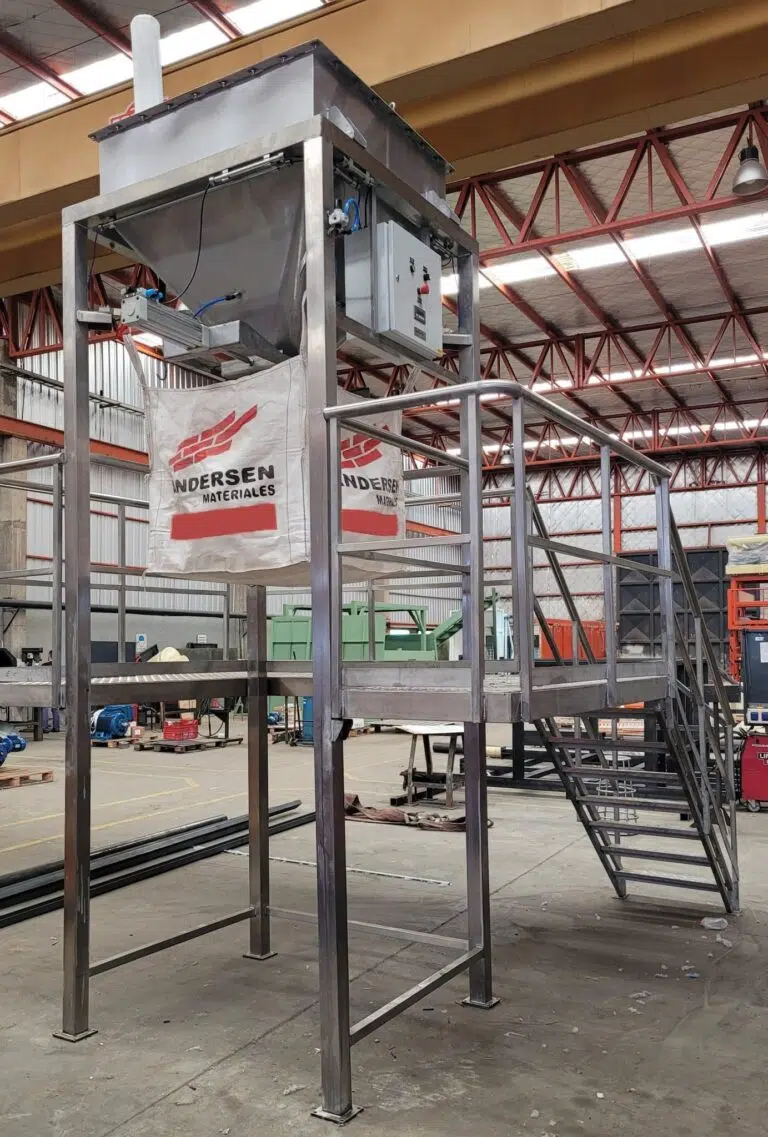

It has a modular height adaptable structure to the big bag that needs to be filled.
It is surrounded by a structure for access to the elements that need to be handled by the operator; such as the placement of the feeding sleeve and the hanging of the ears or handles of the bulk bag. In cases where the pocket is low in height, this structure is not required.
It is possible to connect suction systems.
It can be supplied in both iron and stainless steel.
CBB Big Bag Loader Operation Mode
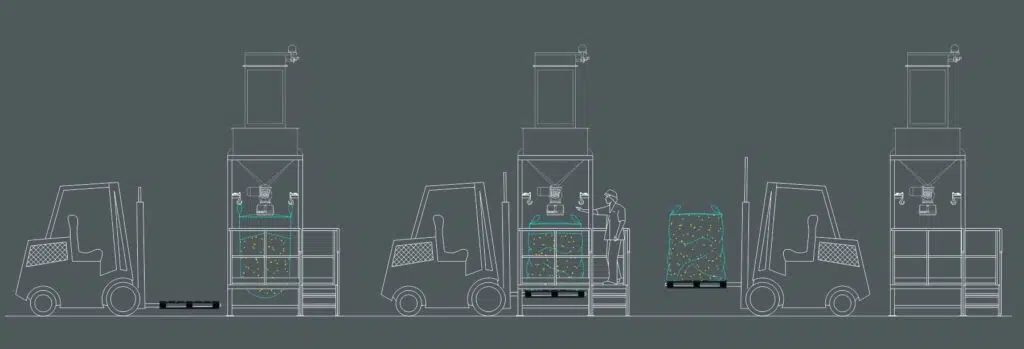
- The operator hangs the big bag, placing his ears on the hooks for them, which the loader has. He also fixes the feeding sleeve to it.
- Filling order is given.
- Once it is full, the forklift with a pallet on its claws approaches and slightly raises the big bag, allowing the operator to unhook it. He also knots his entry sleeve.
- In this way the forklift can take the big bag.
- The operator hangs up a new empty big bag and the cycle starts again. The flow of material to be filled does not stop, since there is an upper tank that stores the product while the bags are changed.
Customary raw materials for bagging:
- Wheat
- Maize
- Oats
- Coffee
- Cocoa
- Rye
- Beat
- Rice
- Girassol
- Chickpeas
- Soybeans
- Peanuts
- Peanuts
- Spices
- Balanced feed
- Pellets or feeds
- Crystalline sugar
- Impalpable sugar
- Cocoa
- Coffee
- Coriander
- Curcuma
- Gelatin
- Bone meal
- Fish flour
- Milk powder
- Dried beans
- Bread crumbs
- Batter
- Aluminum powder
- Atrazine
- Bentonite
- Borax powder
- Lime
- Caolin
- Activated carbon
- Calcium carbonate
- Cement
- Shell
- Quartz
- Titanium Dioxide
- Dolomite
- Fertilizers
- Monoammonium Phosphate
- Diammonium Phosphate
- Tricalcium Phosphate
- Mica
- Refractory Materials
- Sodium naphthalenesulfonate
- Pigments
- Soaps
- Salt
- Precipitated silica
- Caustic soda
- Magnesium sulfate
- Zinc sulfate
- Tanine
- Diatomaceous Earth
- Dyes
- Gypsum
- Lithium
- Afrecho and afrechillo
- Wheat semolina and semolina
- Semolina
- Rebasillo
- Zootechnical flour
- Maize semolina
- Semolina
- Polenta
- Wheat flour, corn flour, soy flour, etc.
- Germ
- Starch
- Hull
- Polycarbonate
- Vinyl polyvinyl chloride or PVC
- Polystyrene or PET
- Polyethylene
- Polypropylene
- Expanded polystyrene (Styrofoam)
- Sawdust
- Wood
- Cork
- Soap poder
- Pigments